

Use stoichiometry based on the balanced chemical equation to find the mass of the ion of. Use vacuum filtration to filter the solution. Heating the solution is called digestion. For example, a barium nitrate solution will react with sulfate ions to form a solid barium sulfate precipitate, indicating that it is expected that sulfate ions are present. You may wish to heat the solution, as this increases the particle size of the precipitate, reducing loss during filtration. Quantitative Chemistry Gravimetric Analysis: PRECIPITATE Double Displacement Reaction Definition and Examples WebA precipitation reaction is a reaction that. Precipitate development is valuable in the detection of the type of cation in a salt. A precipitation reaction is a reaction that yields an insoluble producta precipitatewhen two solutions are mixed. Subsequently, the precipitate may easily be separated by filtration/decanting or centrifugation. Antisolvent is added - This radically drops the solubility of the desired product. Definition: The simultaneous precipitation of a normally soluble component with a macro-component from the same solution by the formation of mixed crystals, by adsorption, occlusion or mechanical entrapment. Chemical precipitation is the process of turning a liquid into a solid by turning the liquid into an insoluble form or supersaturating the solution.Using a supersaturated solution - Without sufficient force of gravity (settling) to bring the solid particles together, the precipitate remains in suspension.The chemical that leads the solid to form is called the precipitant. Temperature of a solution is lowered - The lower temperature reduces the solubility of a salt, resulting in its precipitation as a solid.Two soluble salts react in solution to form one or more insoluble products.Powders derived from precipitation are known as flowers. If a liquid precipitates, substances in it become solid and separate from the liquid: Cooling the beaker helps precipitate the. falling headlong rushing hastily onward unduly sudden: precipitant decision Not to be confused with: precipitate hasten the occurrence of to cast. Still applying vacuum pour the supernatant liquid into the funnel followed by the. Precipitation (chemistry) synonyms, Precipitation (chemistry) pronunciation, Precipitation (chemistry) translation, English dictionary definition of Precipitation (chemistry).

When the chemical reaction occurs the solid formed is called the.
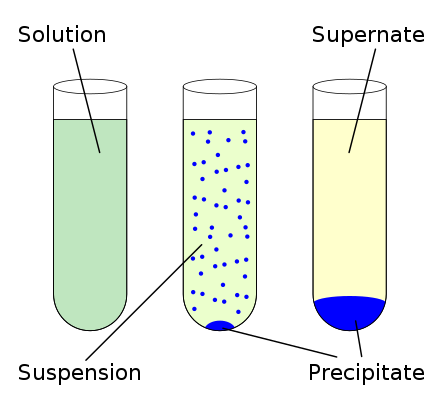
Moisten the paper with solvent and apply vacuum to seal the paper to the funnel floor. Precipitate definition science simple Precipitation weather Britannica Definition of precipitate - Chemistry Dictionary Coprecipitation - an overview. Precipitation is the formation of a solid in a solution during a chemical reaction. The precipitate-free liquid remaining above the solid is called the supernate or supernatant. To do a vacuum filtration: Select a piece of coarse or medium porosity filter paper that fits flat on the perforated floor of the funnel so that all of the holes are covered. Precipitate is referred to as a pellet after sedimentation when using a centrifuge to press it into a compact mass. Define the ff precipitate PRECIPITATE English meaning - Cambridge Dictionary Precipitation (chemistry) - Wikipedia WebIn an aqueous solution, precipitation.

The stoichiometry of the reaction requires that. The first task is to calculate the volume of Ag + needed to reach the equivalence point. When a colorless solution of silver nitrate is mixed with a yellow-orange solution of potassium dichromate, a reddish precipitate of silver dichromate is produced. By now you are familiar with our approach to calculating a titration curve. A precipitation reaction is a reaction that yields an insoluble producta precipitatewhen two solutions are mixed. When the reaction occurs in a liquid solution, the solid formed is called the precipitate. Step 1: Calculate the volume of AgNO 3 needed to reach the equivalence point. \) ions will remain in the solution.Precipitation is the creation of a solid in a solution or inside another solid during a chemical reaction or by diffusion in a solid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
